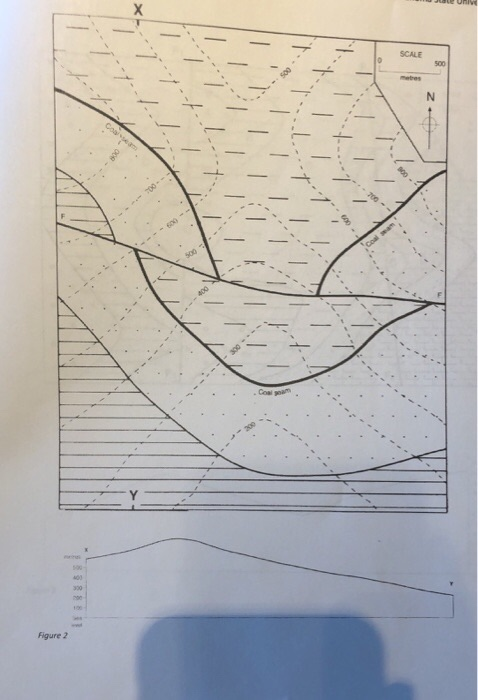
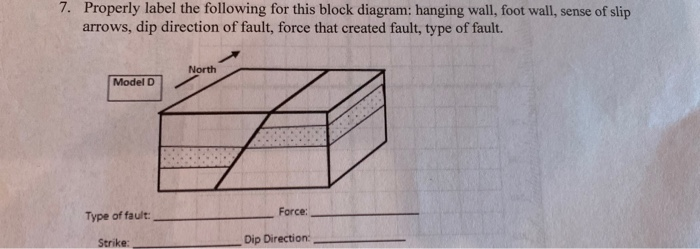
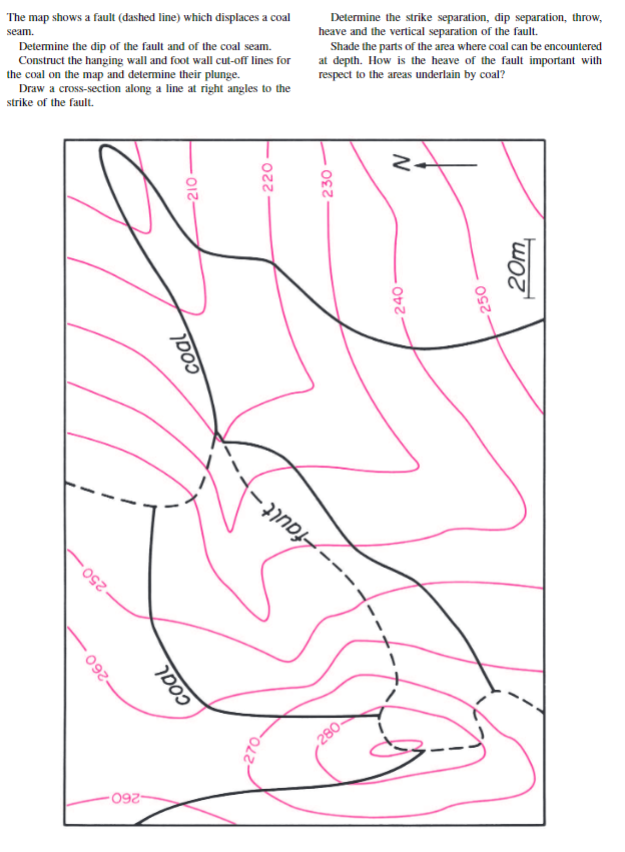
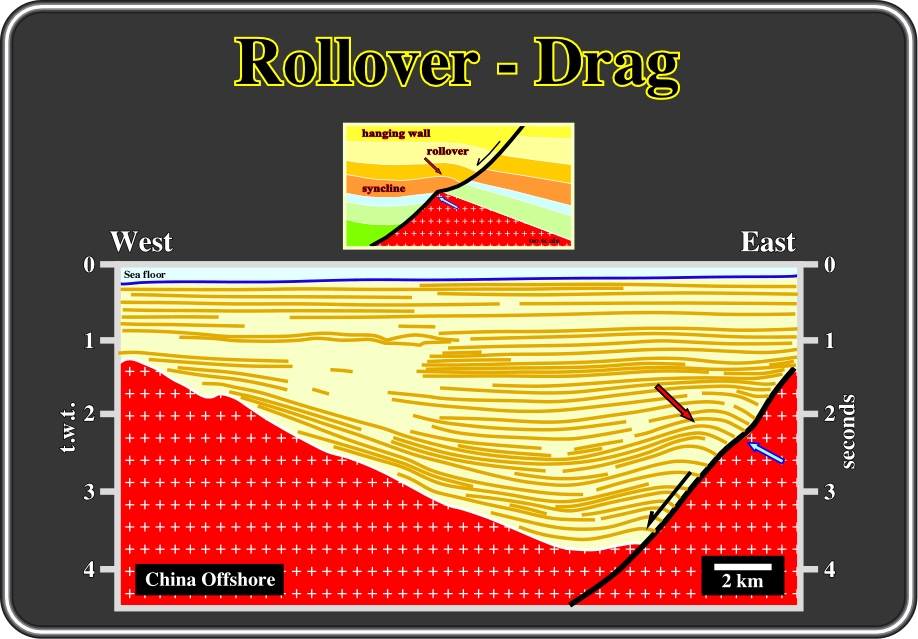
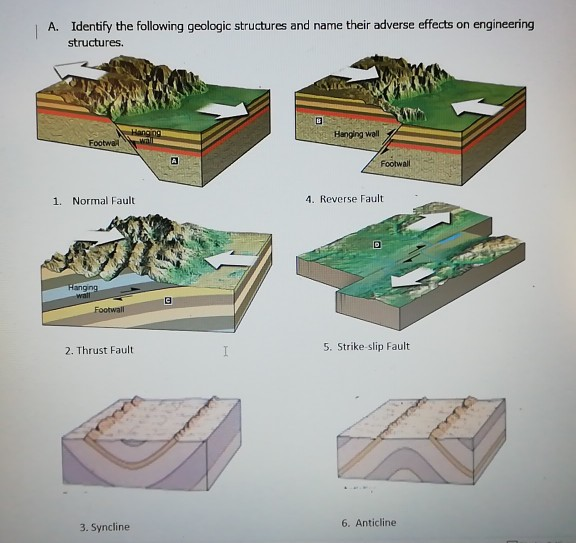
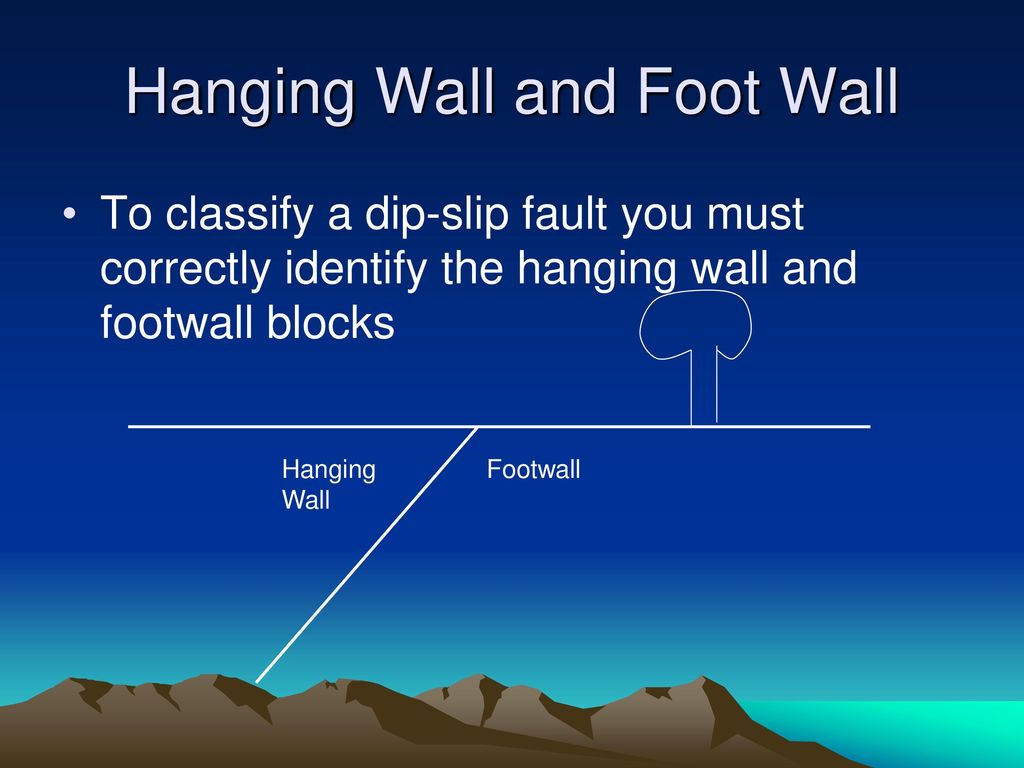
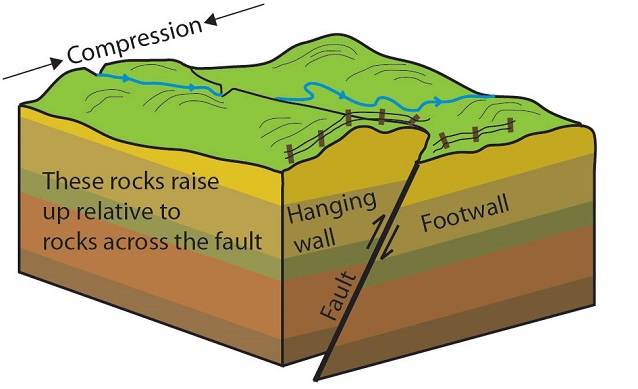
How To Identify Hanging Wall And Footwall

It is a flat surface that may be vertical or sloping.
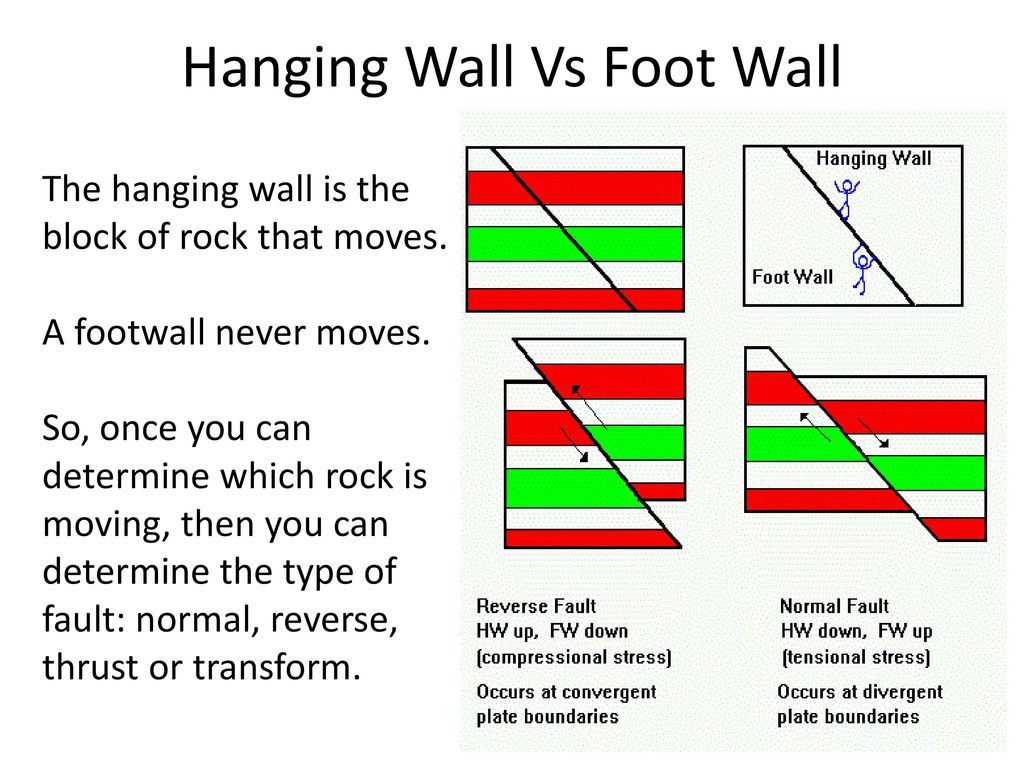
How to identify hanging wall and footwall. But that is when the foot wall moves down the hanging wall moves up. To correctly identify a fault you must first figure out which block is the footwall and which is the hanging wall. Draw a normal and reverse fault label the hanging wall and footwall for each also show how they move for each fault. They bound many of the mountain ranges of the world and many of the rift valleys found along spreading margins.
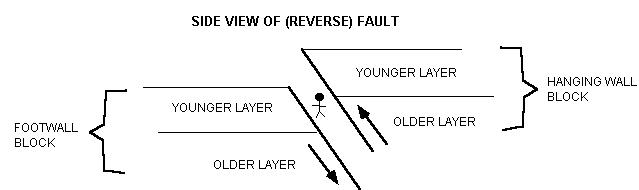
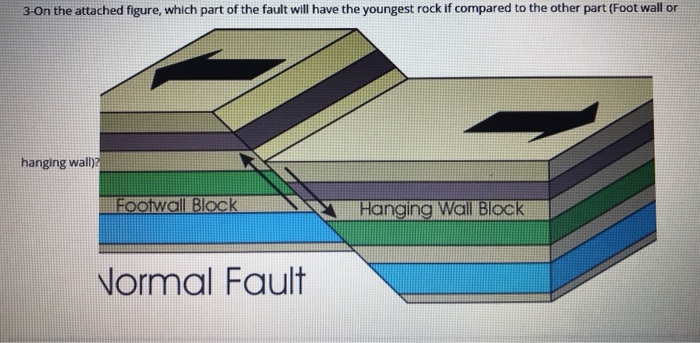
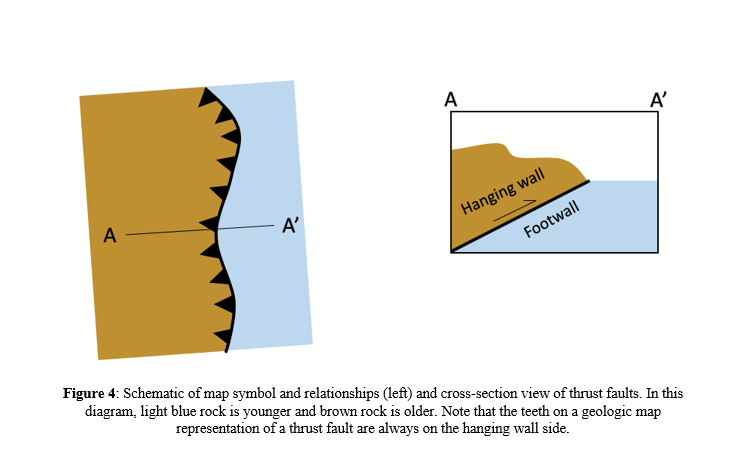
To determine which is which visualize yourself creating a mine in along the fault. Hanging wall and footwall. An arcuate cliff called the headwall. When working a tabular ore body the miner stood with the footwall under his feet and with the hanging wall above him.
The fault plane is where the action is. This terminology comes from mining. The hanging wall slides down relative to the footwall. In an ideal cirque the headwall is semicircular in plan view.
This situation however is generally found only in cirques cut into flat plateaus. The main components of a fault are 1 the fault plane 2 the fault trace 3 the hanging wall and 4 the footwall. More common are headwalls angular in map view due to irregularities in height along. Hanging wall movement determines the geometric classification of faulting.
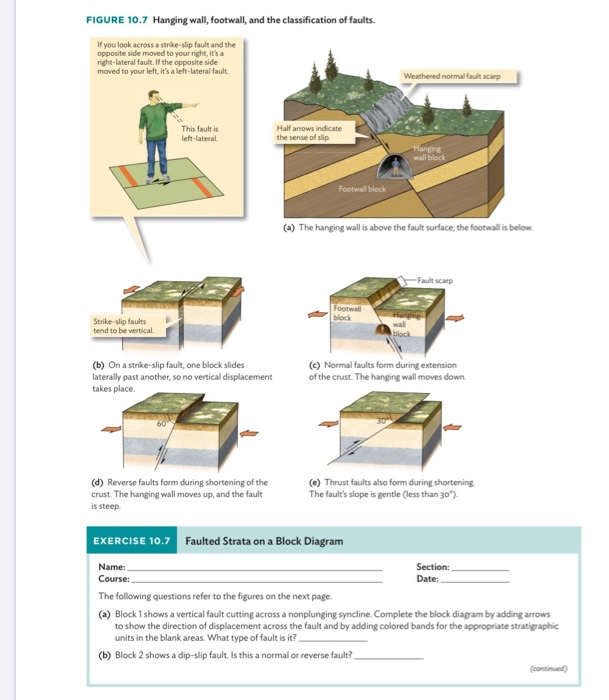
In normal faulting the hanging wall moves downwards in relation to the footwall. In a strike slip fault they slide past each other the foot wall and hanging wall are not there because it has. Normal faults are common. Dip slip movement occurs when the hanging wall moved predominantly up or down relative to the footwall.
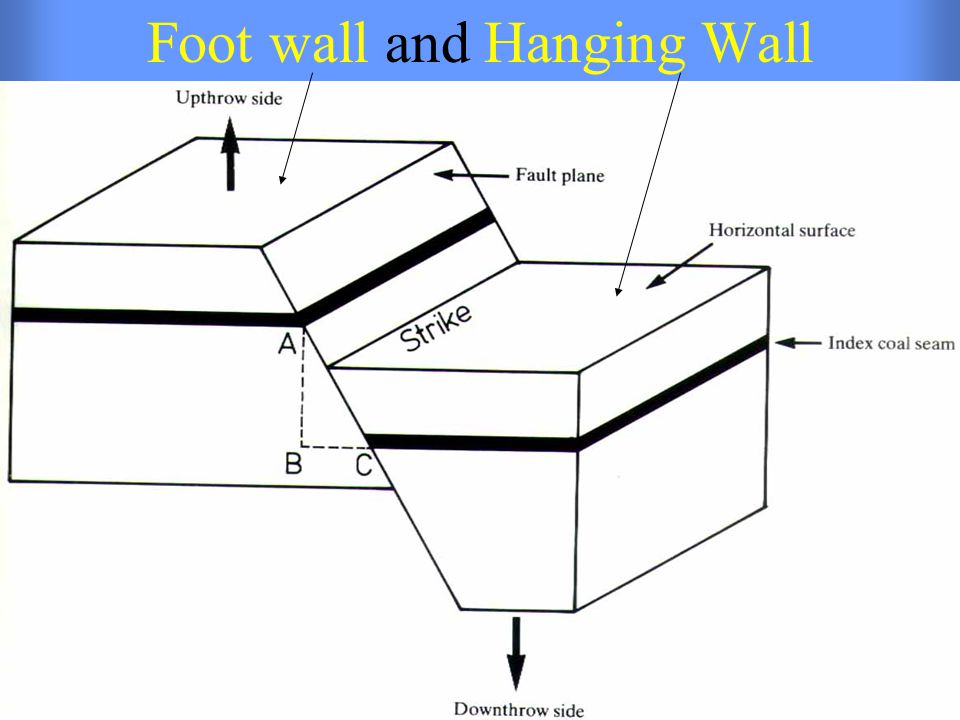
If the motion was down the fault is called a normal fault if the movement was up the. Normal dip slip faults are produced by vertical compression as earth s crust lengthens. The hanging wall occurs above the fault plane and the footwall occurs below it. In a fault plane that dips 45 degrees the overlying rock unit is the hanging wall and the underlying rock unit is the footwall.
The line it makes on the earth s surface is the fault trace. Cirques tarns u shaped valleys arêtes and horns. The hanging wall is above the footwall. Every fault tilted from the vertical has a hanging wall and footwall.
We distinguish between dip slip and strike slip hanging wall movements. Other articles where hanging wall is discussed.