Intersetion Of Two Inclined Sides Of A Roof

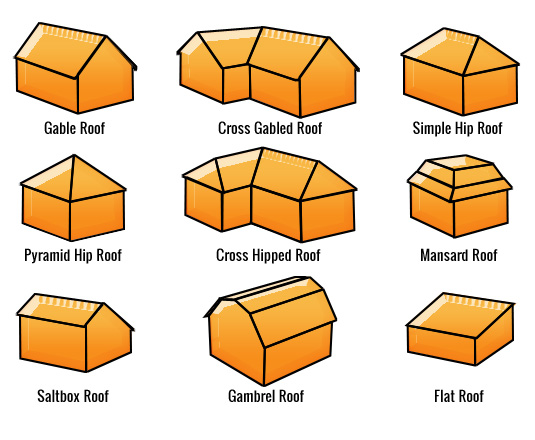
A swedish variant on the monitor roof.
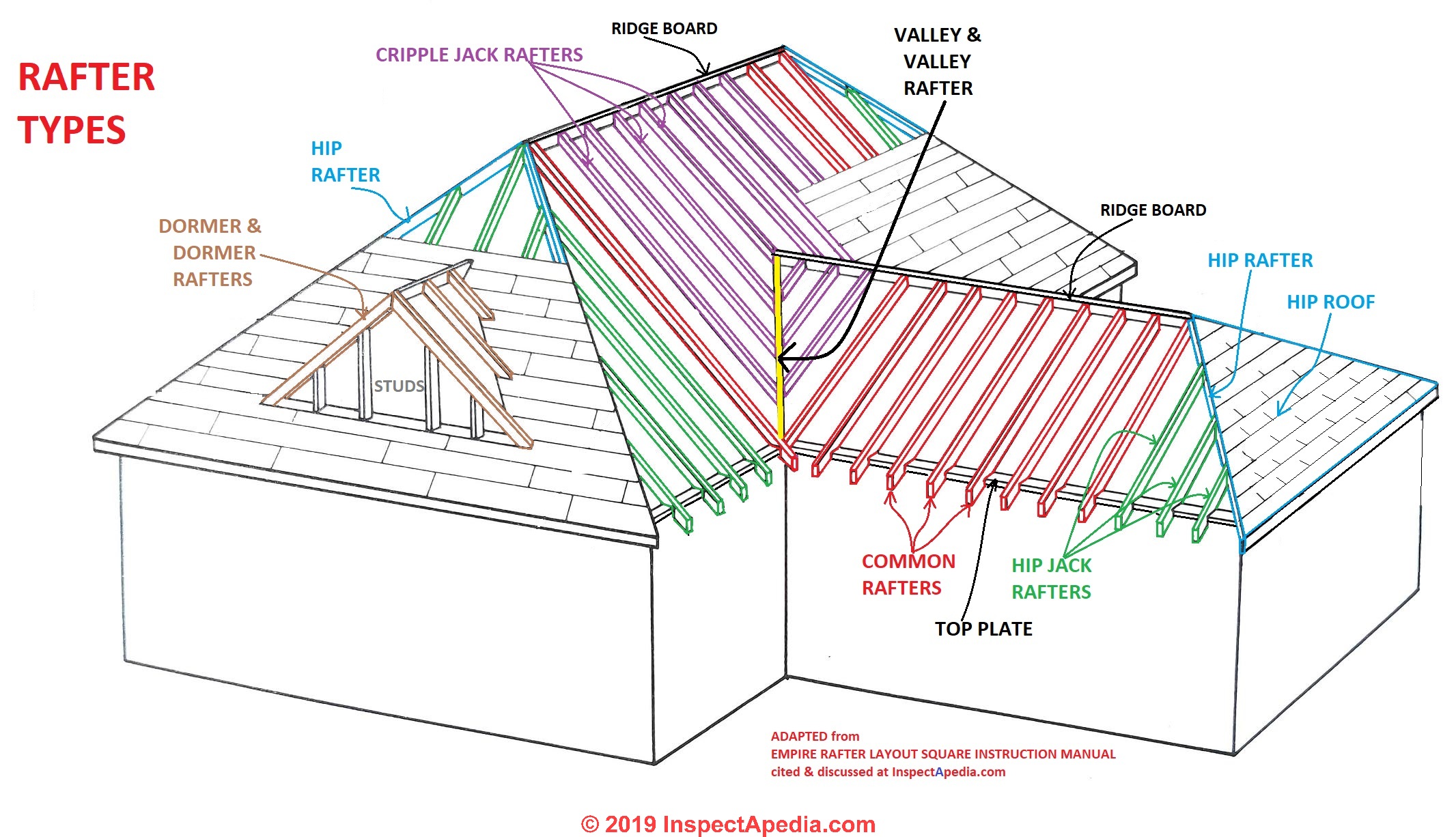
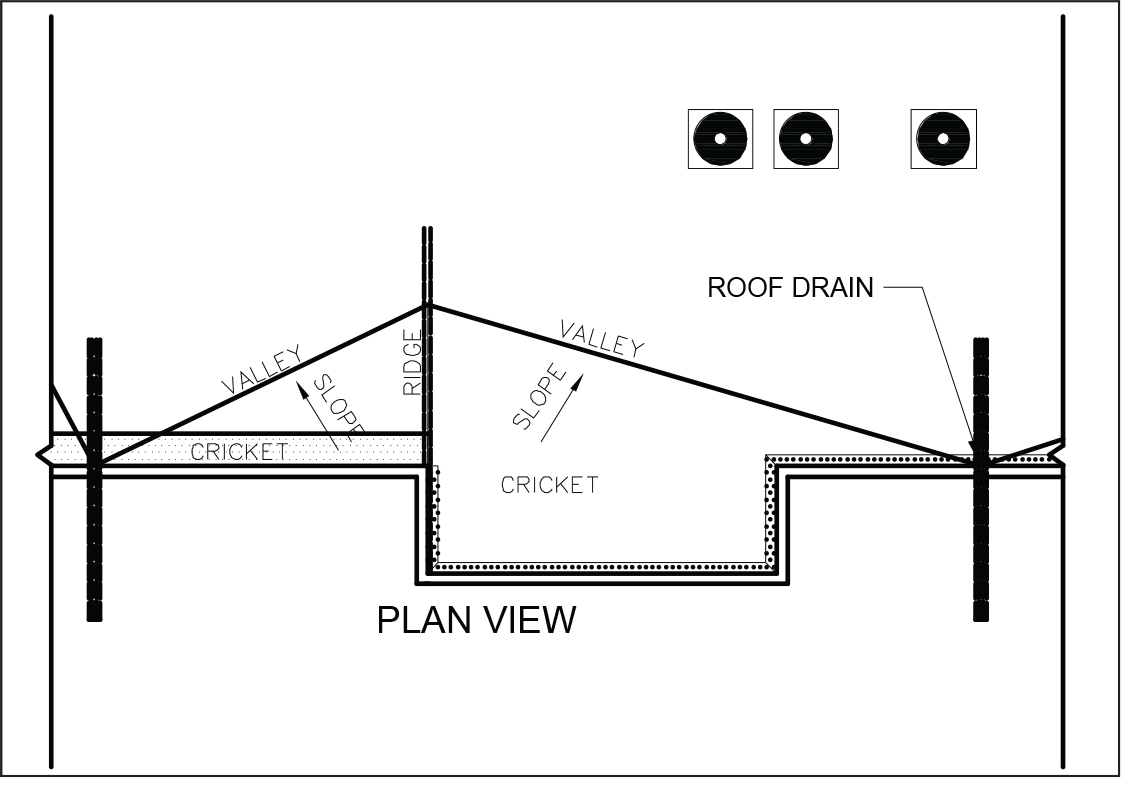
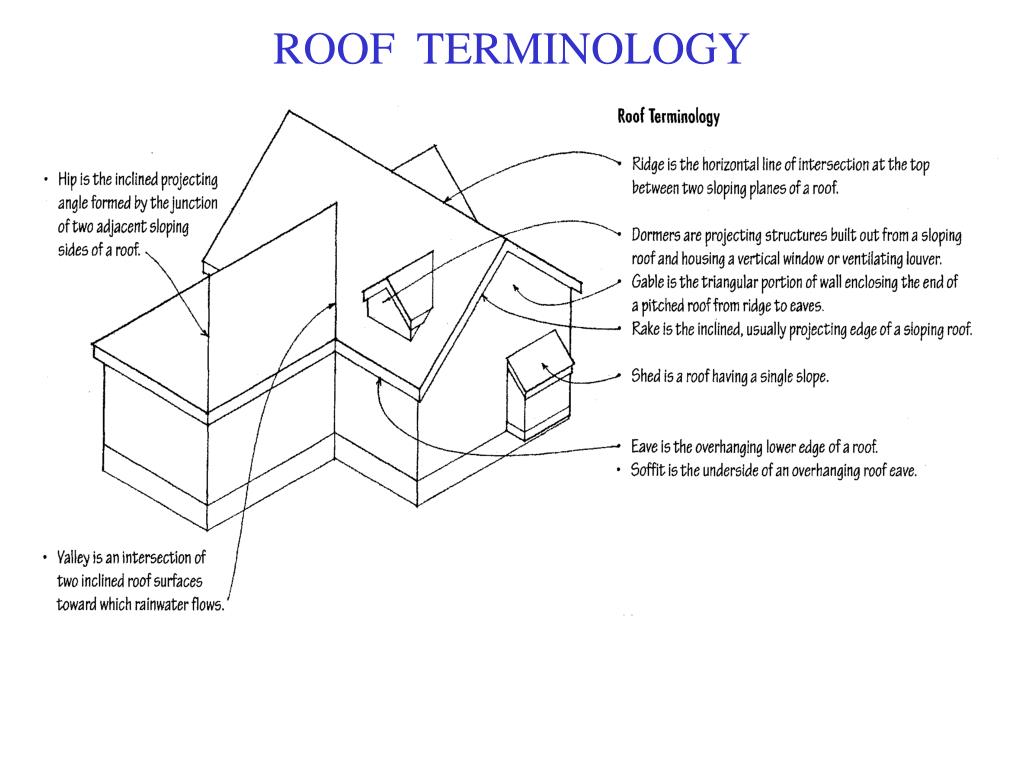
Intersetion of two inclined sides of a roof. Shingles used to cover the inclined external angle formed by the intersection of two sloping roof planes. Runs from the ridge to the eaves. Valley the intersection of two inclined roof surfaces toward w c rainwater flows. A double hip roof with a short vertical wall usually with small windows popular from the 17th century on formal buildings.
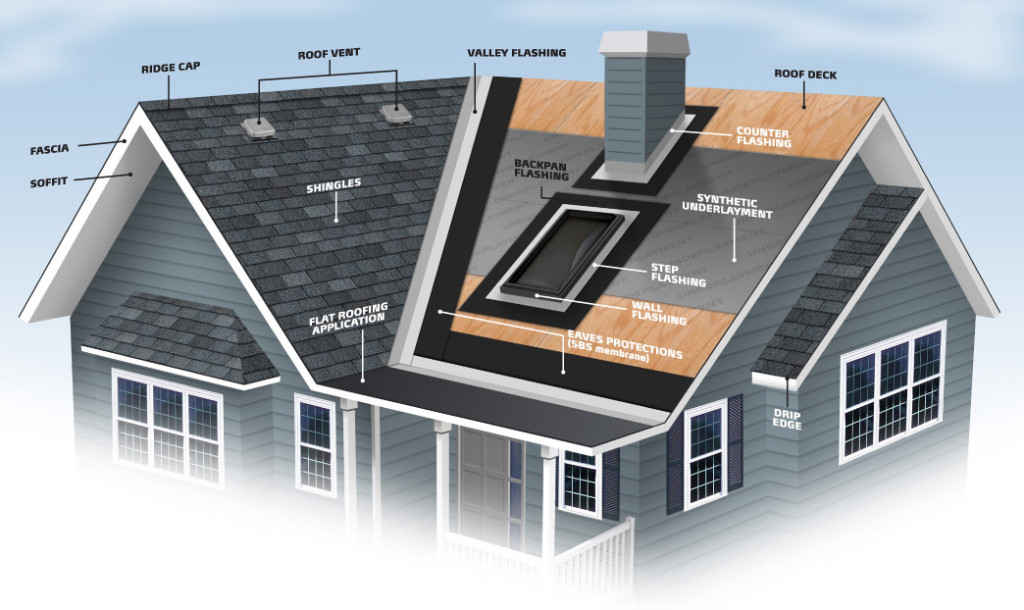
A type of roof containing sloping planes of the same pitch on each of four sides. The inclined projecting angle formed by the junction of two adjacent sloping sides of a roof. A waterproofing seal installed along the roof s valley line with taktekkernbergen no. The horizontal beam connecting two rafters that intersect at the ridge.
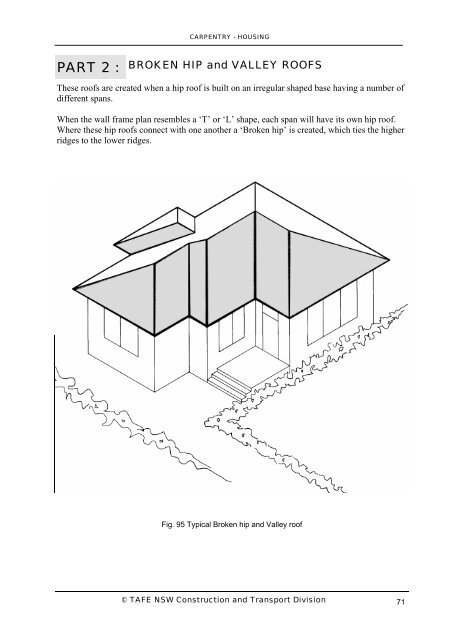
A cross gable roof is a design that consists of two or more gable roof ridges that intersect at an angle most commonly perpendicular to one another. An intersection of two inclined roof surfaces toward which rainwater flows. Connects the rafters near their lower ends and a vertical central member called a king post which connects the apex with the midpoint of the tie beam. The result of joining two or more hip roof sections together forming a t or l shape for the simplest forms or any number of more complex shapes.
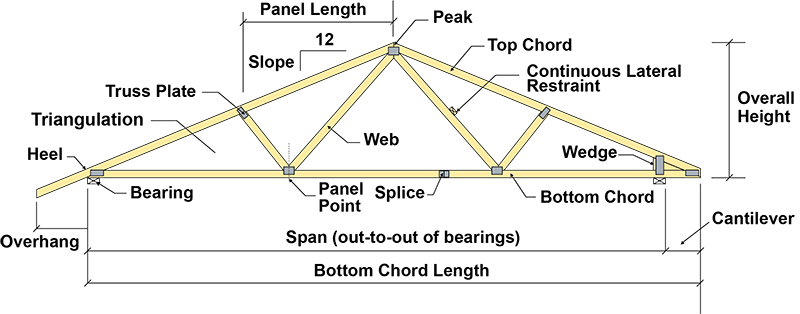
A structural support for a roof formed by two inclined rafters joined at the apex of their intersection. The horizontal external angle formed by the intersection of two sloping roof planes i e. A horizontal tie beam. One of a series of diagonal members of the truss that meet at the apex in order to support the roof deck and its loads.
This type of roof is often seen in buildings with a more complex layout for example homes with an attached garage. The horizontal line of intersection at the top between two sloping planes of a roof. The inclined external angle formed by the intersection of two sloping roof planes.